Cloud Technology
Learn about the basics of cloud computing, the delivery models and the deployments methods.
What is Cloud Computing?
Cloud computing is a game-changer in the Information Technology world and the way we utilise compute services, especially the small and medium businesses. Apart from saving companies huge capital cost, it helps them become agile and respond better to dynamic changes.
Even though the term cloud technology seems like a new buzzword, it is an evolution of technology over time; we have been using and adapting it from the early 2000s in the form of an email account.
In simple terms, cloud computing implies storing and accessing data and software over the Internet instead of the computers hard drive, replacing the traditional hardware heavy approach to technology. In technical terms, it is the ability to leverage remote systems on an on-demand basis over the open Internet. For Eg, we leverage computer resources as we do websites, we're able to get into a system - Log on, and access resources such as storage, compute, machine learning systems, databases and more such services provided by data centers. It gives the ability to pay for only the resources used along with the facility to scale up and scale back as required.
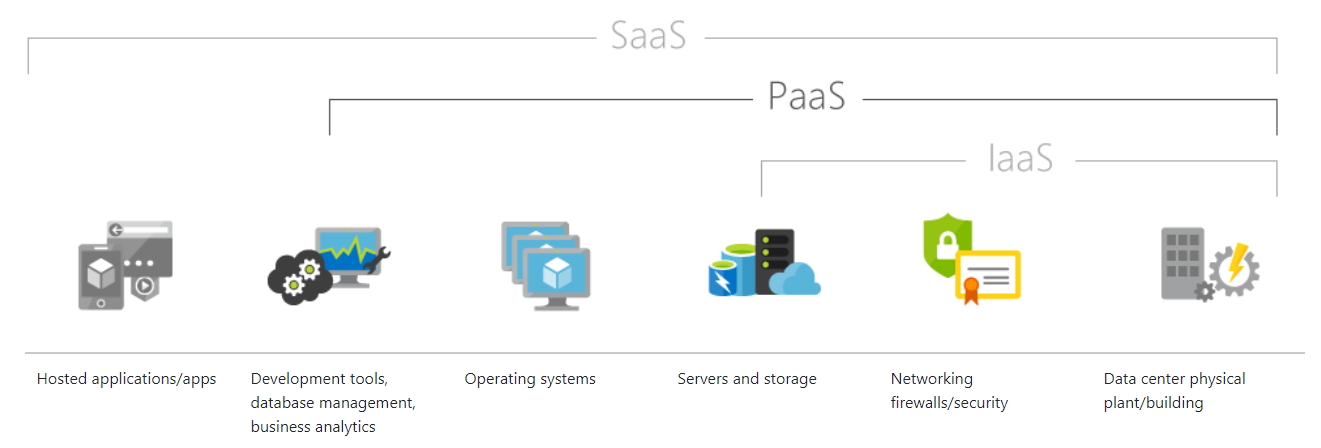
Source : Internet
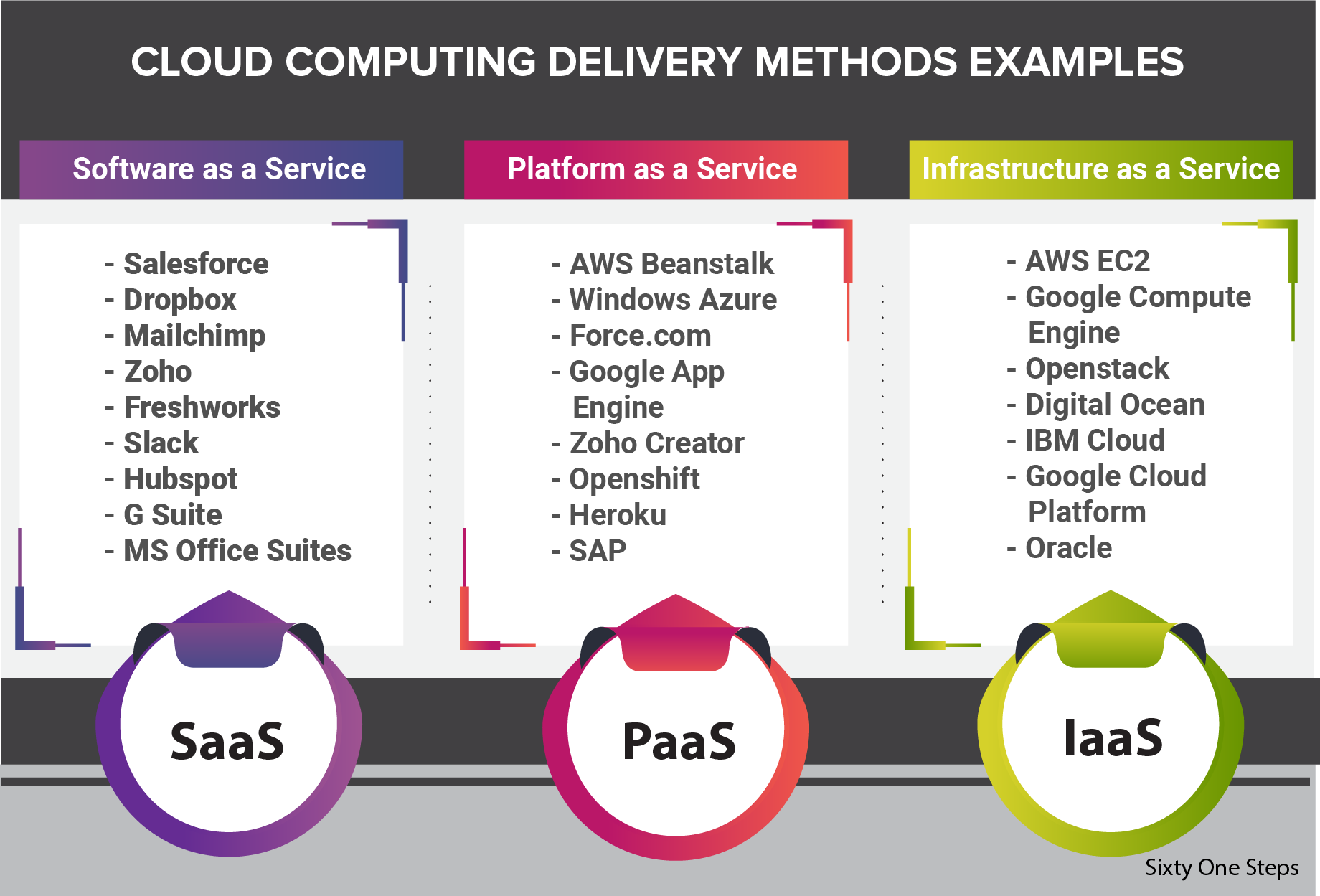
Three Delivery Models of Cloud Computing - SaaS, PaaS, IaaS & Serverless Computing
SaaS - Software as a Service
SaaS presents a complete software solution available to be used on a pay-as-you-go basis of a cloud service provider. Users can connect to a rented app over the Internet, usually with a web browser. All of the underlying middleware, infrastructure, app data and app software are placed in the service provider's data center. The service provider handles software and the hardware and with the relevant service agreement to ensure the security and availability of the app and data. SaaS enables an organisation to get instantly up and running with an app at the smallest upfront cost.
Benefits of adapting the business to SaaS Products
- Huge Saving
- Simple Maintenance
- Less work for IT Teams
- Ideal for Remote Teams
- No / Less Investment physical servers
PaaS - Platform as a Service
Platform as a service point to cloud computing services that provide an on-demand environment for testing, developing, managing and delivering software applications. PaaS is designed for developers to easily and quickly create web or mobile apps, without worrying about investing or maintaining the underlying infrastructure of servers, network, storage and databases required for the development.
Common PaaS scenarios
- Built-in software components
- Analytics or business intelligence.
- Workflow, security directory, and scheduling.
Serverless Computing
Along with PaaS, serverless computing concentrates on building app functionality without spending time, continually managing the servers and infrastructure needed to do so. The cloud provider manages the setup, capability planning and server management. Serverless architectures are very scalable and event-driven, solely utilising resources when a precise function or trigger happens.
IaaS - Infrastructure as a Service
IaaS quickly scales up and down with request, allowing you to pay only for whatever you use. It helps evade the expense and complexity of purchasing and managing its physical servers and separate datacenter infrastructure. Each resource is proposed as a separate service component, that can be rented for as long as required.
IaaS Functionalities used by businesses
- Web apps
- Website hosting
- Big data analysis
- Test and development
- Storage, backup and recovery
- High-performance computing
Cloud Computing Deployment Models - Private, Public and Hybrid.
Cloud computing requirements vary from each company. Many different models, classes and services have developed to help give the right solution. Determining the type of cloud deployment to be implemented is a vital step. There are three distinct ways to deploy cloud services: on a public cloud, private cloud or hybrid cloud.
Public cloud
Public clouds are maintained and operated by a third-party cloud service providers, which present their computing resources like servers and storage across the Internet. Public cloud suggests all hardware, software and other supporting infrastructure are owned and managed by the cloud provider. These services can be accessed and managed using a web browser.
Private cloud
A private cloud attributes to cloud computing resources handled exclusively by a particular business or organisation. A private cloud can be physically placed on the organisation's on-site data center. Few companies also compensate third-party service providers for hosting their private cloud. In a private cloud, infrastructure and the services are managed on a private network.
Hybrid cloud
Hybrid clouds blend public and private clouds, connected by technology that allows data and applications to be shared between them. By allowing data and applications to move within private and public clouds, a hybrid cloud provides your business higher flexibility, more deployment choices and aids optimise your existing security, infrastructure, and compliance.
More from Sixty One Steps

Migrate Away From Spreadsheets
Learn about success, application and why its time to move on from spreadsheets to holistic data management.
⟵ PreviousMSME Digital Transformation
Learn more about Micro, Small and Medium Businesses adoption of Technology.
Next ⟶Sixty One Steps
We empower brands to adopt technology in the age of digital transformation as Zoho Partners Chennai.

Get in touch
Tel: +91 99620 61061
Drop us an email at: hello@sixtyonesteps.com
Find us
Sixty One Steps Advertising Pvt LtdW660, IVth Ave, Anna Nagar West Extn
Chennai - 600101, TN, India.